Extraction Optimization and Structural and Thermal Characterization of the Antimicrobial Abietane 7α-Acetoxy-6β-hydroxyroyleanone
C.E.S. Bernardes, C. Garcia, F. Pereira, J. Mota, P. Pereira, M.J. Cebola, et. al.
Mol. Pharmaceutics 2018, 15, 1412-1419.
Abstract
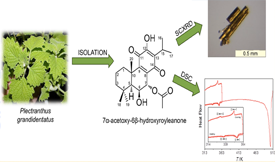
The abietane 7α-acetoxy-6β-hydroxyroyleanone (AHR), obtained from plant extracts, is an attractive lead for drug development, given its known antimicrobial properties. Two basic requirements to establish any compound as a new drug are the development of a convenient extraction process and the characterization of its structural and thermal properties. In this work seven different methods were tested to optimize the extraction of AHR from Plectranthus grandidentatus. Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) proved to be the method of choice, delivering an amount of AHR (57.351 μg·mg−1) approximately six times higher than the second best method (maceration in acetone; 9.77 μg·mg−1). Single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis of the ARH molecular and crystal structure carried out at 167±2 K and 296±2 K showed only a single phase, here dubbed form III (orthorhombic space group P21212), at those temperatures. The presence of two other polymorphs above room temperature was, however, evidenced by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The three forms are enantiotropically related, with the form III → form II and form II → form I transitions occurring at 333.5±1.6 K and 352.0±1.6 K, respectively. The fact that the transitions are reversible suggests that polymorphism is not likely to be an issue in the development pharmaceutical formulations based on ARH. DSC experiments also showed that the compound decomposes on melting at 500.8±0.8 K. Melting should therefore be avoided if, for example, strategies to improve solubility based on the production of glassy materials or solid dispersions are considered.
Return Previous Next